一. 目的 创建一个线程池管理模块,他仅需要满足如下功能即可:
创建一个支持N线程的线程池
销毁一个线程池
线程池中的线程数量可动态调整
可以向线程池中添加任务
二. 总体设计 每个线程交给一个worker的结构体进行管理,创建一个线程池就是创建一个worker队列,在对线程池进行CRUD时需要使用线程锁来保护数据。
我们希望创建的线程阻塞在一个名为“job add”的信号上,只有我们为线程池添加任务的时候,线程才会去真正执行这个任务。
我们将新创建的任务称为job,并存储在一个名为job的队列中,当为线程池添加任务的时候,就把任务入队,并且广播这个事件。
线程池中线程数量的调整是一个特殊的job。
我们希望在销毁线程池的时候终止所有job,并释放相关资源,所以针对job,他需要有一个cancel()的方法,在线程退出后我们希望他要尝试向主线程发送一个终止信号,以便主线程进行资源的回收。
三. 详细设计 3.1 结构体设计 我们将从小到大,来设计整个模块中的结构体 。
1. 工作项 job用来描述用户提供的任务,每个任务都应该有自己的执行状态、执行函数、取消函数、销毁函数 。所以我们将他设计为如下结构。
status字段表示当前的job进行到什么阶段了。也是被线程池调度时关键的参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 typedef struct job_t job_t ;typedef enum job_status_t job_status_t ;enum job_status_t { JOB_STATUS_QUEUED = 0 , JOB_STATUS_EXECUTING, JOB_STATUS_CANCELED, JOB_STATUS_DONE, }; struct job_t { job_status_t status; bool (*cancel)(job_t *this); void (*execute)(job_t *this); void (*destory)(job_t *this); };
为了管理多任务,我们job保存在一个队列中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef struct job_queue job_q_t ;struct job_entry { job_t job; TAILQ_ENTRY(job_entry); }; TAILQ_HEAD(job_queue, job_entry);
2. 异步执行环境 我们希望有一个结构体可以用来描述一个线程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef void *(*thread_main_t )(void *arg);typedef struct thread_t thread_t ;struct thread_t { pthread_t tid; thread_main_t main; void *arg; };
3. 工作队列
节点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct worker_thread_t { processor_t *processor; job_t *job; thread_t *thread; };
这里使用的<sys/queue.h>提供的TAILQ队列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef struct thread_queue thread_q_t ;struct worker_entry { worker_thread_t worker; TAILQ_ENTRY(worker_entry) entries; }; TAILQ_HEAD(thread_queue, worker_entry);
4. 线程池 线程池需要一些统计量来保存当前线程池状态,例如当前线程池线程数量,期望线程数量,执行工作的线程数量,一个管理线程的队列,一个管理任务的队列,一个保护线程池的锁,一个新增任务的信号。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 typedef struct processor_t processor_t ;struct processor_t { int total_threads; int desired_threads; int working_threads; thread_q_t threads; job_q_t jobs; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t job_add; };
3.2 接口设计 本节将从上到下来设计所需要的接口
1. 线程池 创建线程池,取消所有worker线程,销毁线程池,配置线程池:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 processor_t *processor_create(); struct processor_t { /* public interface */ void (*set_threads)(processor_t *this, int count); void (*cancel)(processor_t *this); void (*destory)(processor_t *this); /* private member */ };
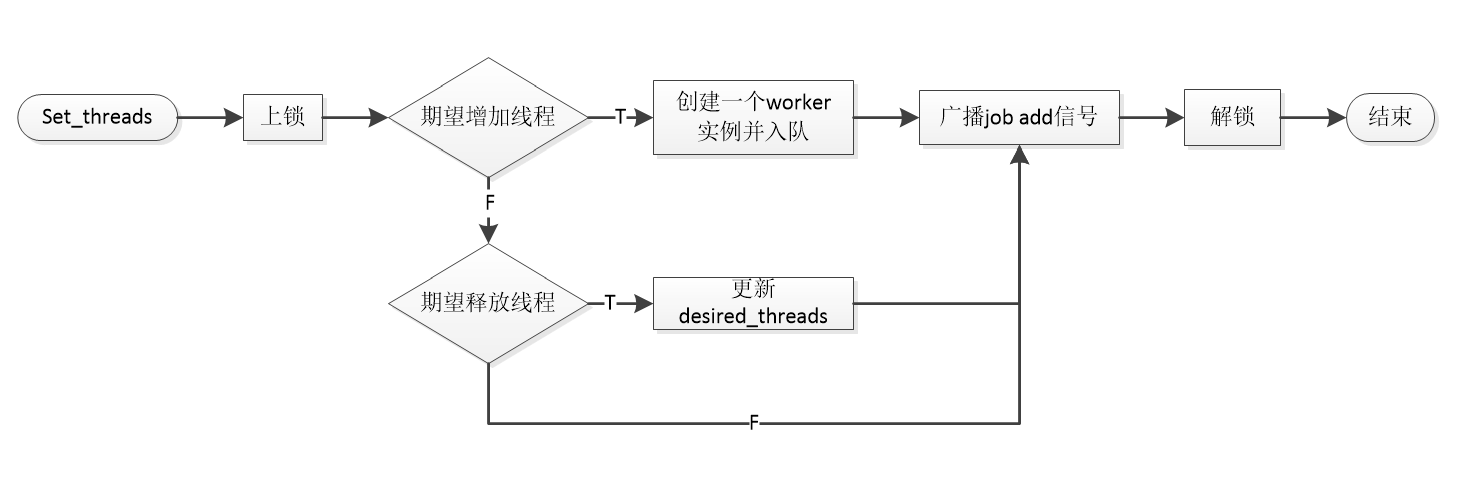
set_threads()将创建count个worker线程,每个worker线程阻塞等待job add信号。这里需要注意,不论是创建worker还是期望释放线程,都会广播job_add信号,结合process_jobs函数(后面会提到),就可以实现线程数的调整。
1 static void __processor_set_threads(processor_t *this, int count)
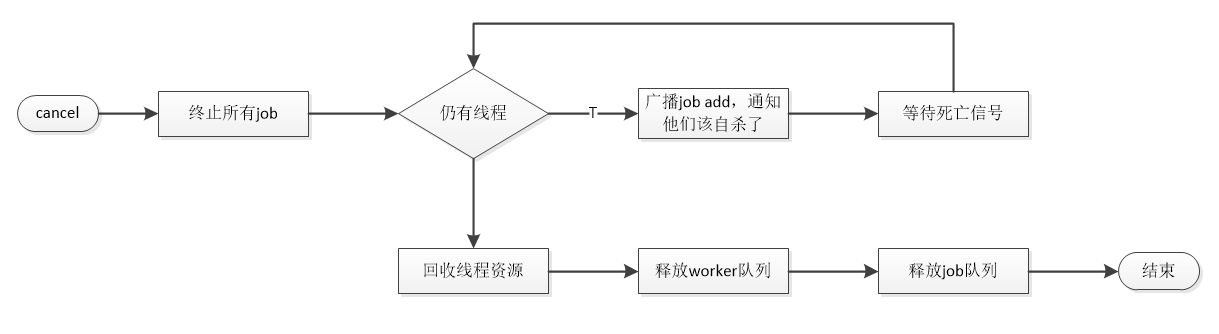
cancel()将期望子线程数归零,并通知每个job取消执行任务,并阻塞在一个线程终止信号上,如果等到当前子线程数归零,则开始回收线程资源,并释放worker队列和job队列。
2. 创建线程实例 每个worker entry就代表一个线程实例。
1 static struct worker_entry *worker_create (processor_t *processor, thread_main_t main)
在这个函数中,我们会对worker_entry结构体中的字段进行初始化,核心的动作是创建一个线程实例,该线程实例将会调用第二个参数main所指的回调函数。
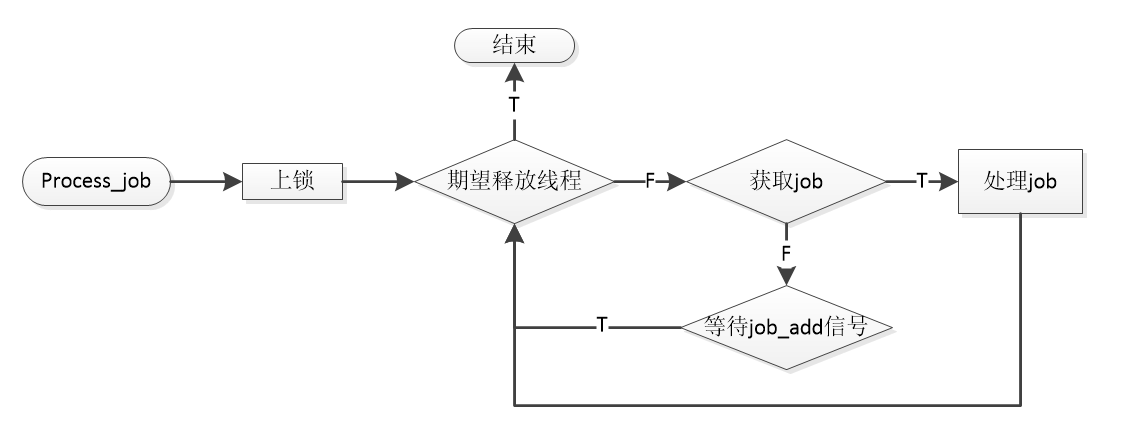
由于我们的worker要做的事情是等待job_add的信号,有job的时候去处理他,这也是线程池中的一个核心函数,我们会从job队列中取出job,并且去执行这个job。
由于在set_threads的时候会广播job_add信号,所以所有空闲的线程都会收到,如果发现我们期望释放这个线程,那么这个线程就会退出,实现了线程数量的调整。
1 static void *process_jobs (worker_thread_t *worker)
3. thread 这里仅仅是对pthread_create()的一层封装,期间会为thread_t结构体做初始化。有了这一层,我们可以对thread进行更好的控制,例如对线程清理函数的注册等,当然这些都是后话,未来会逐渐完善这些东西,目前我们只是打印当前线程的TID而已。
1 static thread_t *thread_create (thread_main_t main, worker_thread_t *worker) ;
4. job 每个job代表用户期待要执行的任务,用户在创建job时就需要为他注册相关执行、取消、销毁函数。方便线程池进行管理。
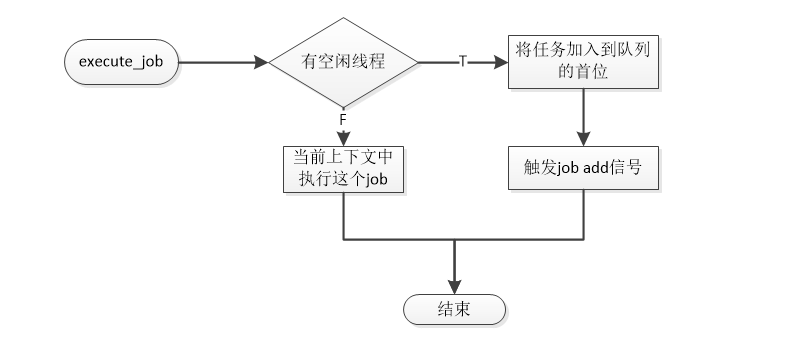
在这里引入线程池对job的两个方法:queue_job()和execute_job(),前者仅仅job入队,是否会被线程池调用取决于当先线程池是否有资源来出队这个job并去执行它。而后者会先查询当前是否有空闲线程,如果有,则将这个job加入到队列的首位,让他优先被执行。否则的话将在当前上下文中去执行这个job。
1 2 static void __processor_queue_job(processor_t *this, struct job_entry *entry);static void __processor_execute_job(processor_t *this, struct job_entry *entry);
3.3 任务调度 我们现在有了线程池,有了将任务入队的接口,那么接下来就要分析下如果将任务出队并且来执行他们了。
1. 出队 这个很简单,由于我们此时已经持有锁了,可以直接出队。
1 static bool get_job (processor_t *processor, worker_thread_t *worker) ;
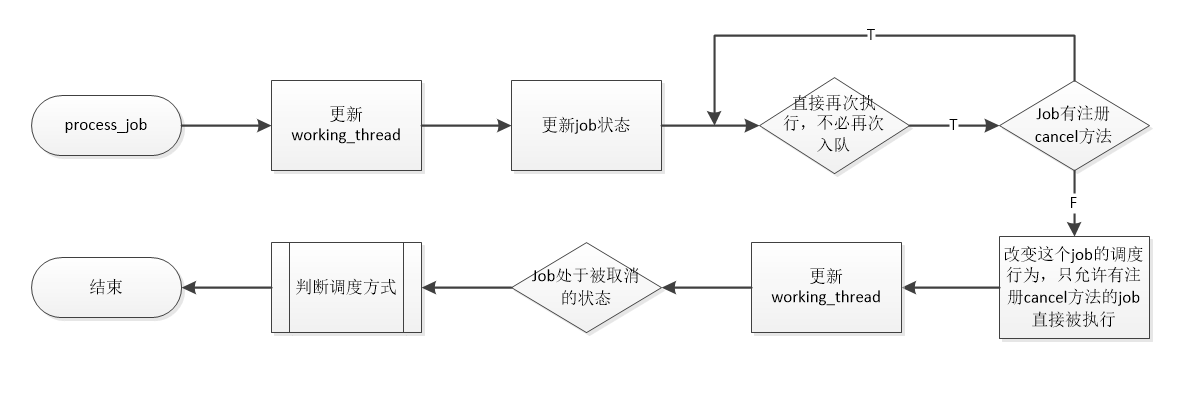
2. 调度 这是任务调度的一个核心函数。非常关键。
1 static void process_job (processor_t *processor, worker_thread_t *worker) ;
在描述这一段之前,我们要解释下job的一个属性——调度状态。
job的exec方法进行优化,它返回值值将被用于判断调度行为。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 typedef enum job_requeue_type_t job_requeue_type_t ;typedef struct job_requeue_t job_requeue_t ;enum job_requeue_type_t { JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_NONE = 0 , JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_FAIR, JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_DIRECT, JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_SCHEDULE, }; struct job_requeue_t { job_requeue_type_t type; unsigned int rel; };
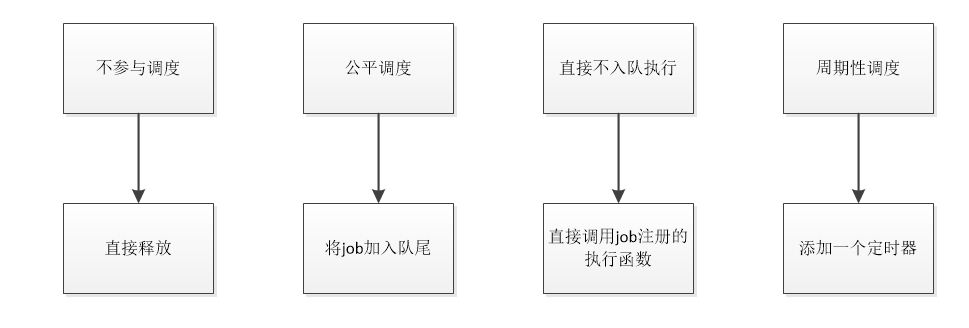
我们将job的调度状态分为四种。不调度直接释放、公平调度、不入队直接再次执行、周期性调度。
四. 源码 threads_pool_00.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #ifndef __THREADS_POOL_00_H__ #define __THREADS_POOL_00_H__ #include <pthread.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <sys/queue.h> typedef void *(*thread_main_t )(void *arg);typedef struct processor_t processor_t ;typedef struct thread_t thread_t ;typedef struct worker_thread_t worker_thread_t ;typedef enum job_status_t job_status_t ;typedef enum job_requeue_type_t job_requeue_type_t ;typedef struct job_requeue_t job_requeue_t ;typedef struct job_t job_t ;typedef struct job_queue job_q_t ;typedef struct thread_queue thread_q_t ;struct thread_t { pthread_t tid; thread_main_t main; void *arg; }; enum job_status_t { JOB_STATUS_QUEUED = 0 , JOB_STATUS_EXECUTING, JOB_STATUS_CANCELED, JOB_STATUS_DONE, }; enum job_requeue_type_t { JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_NONE = 0 , JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_FAIR, JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_DIRECT, JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_SCHEDULE, }; struct job_requeue_t { job_requeue_type_t type; unsigned int rel; }; struct job_t { job_status_t status; bool (*cancel)(job_t *this); job_requeue_t (*execute)(job_t *this); void (*destory)(job_t *this); }; struct job_entry { job_t *job; TAILQ_ENTRY(job_entry) entries; }; TAILQ_HEAD(job_queue, job_entry); struct worker_thread_t { processor_t *processor; job_t *job; thread_t *thread; }; struct worker_entry { worker_thread_t worker; TAILQ_ENTRY(worker_entry) entries; }; TAILQ_HEAD(thread_queue, worker_entry); struct processor_t { void (*set_threads)(processor_t *this, int count); void (*queue_job) (processor_t *this, struct job_entry *job_entry); void (*execute_job)(processor_t *this, struct job_entry *job_entry); void (*cancel)(processor_t *this); void (*destory)(processor_t *this); int total_threads; int desired_threads; int working_threads; thread_q_t threads; job_q_t jobs; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t job_add; pthread_cond_t thread_terminated; }; processor_t *processor_create () ;#endif
threads_pool_00.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 #include "threads_pool_00.h" #include <pthread.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/queue.h> #include <unistd.h> static void *thread_main (thread_t *this) { void *res; res = this->main(this->arg); return res; } static thread_t *thread_create (thread_main_t main, worker_thread_t *worker) { thread_t *this = calloc (1 , sizeof (*this)); this->main = main; this->arg = worker; if (pthread_create(&this->tid, NULL , (void *)thread_main, this) != 0 ) { free (this); return NULL ; } return this; } static struct worker_entry *worker_create (processor_t *processor, thread_main_t main) { struct worker_entry *entry =calloc (1 , sizeof (*entry)); entry->worker.processor = processor; entry->worker.thread = thread_create(main, &entry->worker); if (entry->worker.thread == NULL ) { fprintf (stderr , "create thread failed!\n" ); free (entry); return NULL ; } return entry; } static void __processor_cancel(processor_t *this){ struct worker_entry *worker , *worker_del ; struct job_entry *job , *job_del ; pthread_mutex_lock(&this->mutex); this->desired_threads = 0 ; worker = TAILQ_FIRST(&this->threads); while (worker) { if (worker->worker.job && worker->worker.job->cancel) { if (!worker->worker.job->cancel(worker->worker.job)) { pthread_cancel(worker->worker.thread->tid); } } worker = TAILQ_NEXT(worker, entries); } while (this->total_threads > 0 ) { pthread_cond_broadcast(&this->job_add); pthread_cond_wait(&this->thread_terminated, &this->mutex); } worker_del = TAILQ_FIRST(&this->threads); while (worker_del) { worker = TAILQ_NEXT(worker_del, entries); pthread_join(worker_del->worker.thread->tid, NULL ); free (worker_del->worker.thread); free (worker_del); worker_del = worker; } job_del = TAILQ_FIRST(&this->jobs); while (job_del) { job = TAILQ_NEXT(job_del, entries); printf ("destory\n" ); job_del->job->destory(job_del->job); free (job_del); job_del = job; } pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->mutex); } static void __processor_destory(processor_t *this){ __processor_cancel(this); pthread_mutex_destroy(&this->mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&this->job_add); free (this); } static bool get_job (processor_t *processor, worker_thread_t *worker) { struct job_entry *job_entry ; job_entry = TAILQ_FIRST(&processor->jobs); if (job_entry) { TAILQ_REMOVE(&processor->jobs, job_entry, entries); worker->job = job_entry->job; free (job_entry); return true ; } return false ; } static void process_job (processor_t *processor, worker_thread_t *worker) { job_requeue_t requeue; struct job_entry *job_entry ; job_t *this_job, *to_destory; this_job = worker->job; to_destory = NULL ; processor->working_threads++; this_job->status = JOB_STATUS_EXECUTING; pthread_mutex_unlock(&processor->mutex); while (true ) { requeue = this_job->execute(this_job); if (requeue.type != JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_DIRECT) { break ; } else if (!this_job->cancel) { requeue.type = JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_FAIR; break ; } } pthread_mutex_lock(&processor->mutex); processor->working_threads--; if (this_job->status == JOB_STATUS_CANCELED) { to_destory = this_job; } else { switch (requeue.type) { case JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_NONE: this_job->status = JOB_STATUS_DONE; to_destory = this_job; break ; case JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_FAIR: this_job->status = JOB_STATUS_QUEUED; job_entry = calloc (1 , sizeof (*job_entry)); job_entry->job = this_job; TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&processor->jobs, job_entry, entries); pthread_cond_signal(&processor->job_add); break ; case JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_SCHEDULE: printf ("add a timer thread\n" ); break ; default : break ; } } worker->job = NULL ; if (to_destory) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&processor->mutex); to_destory->destory(to_destory); pthread_mutex_lock(&processor->mutex); } return ; } static void *process_jobs (worker_thread_t *worker) { processor_t *processor = worker->processor; pthread_mutex_lock(&processor->mutex); while (processor->desired_threads >= processor->total_threads) { if (get_job(processor, worker)) { process_job(processor, worker); } else { pthread_cond_wait(&processor->job_add, &processor->mutex); } } processor->total_threads--; pthread_cond_signal(&processor->thread_terminated); pthread_mutex_unlock(&processor->mutex); return NULL ; } static void __processor_set_threads(processor_t *this, int count){ pthread_mutex_lock(&this->mutex); if (count > this->total_threads) { struct worker_entry *entry ; this->desired_threads = count; #if 0 while (count > this->total_threads) { entry = worker_create(this, NULL ); if (entry) { TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&this->threads, entry, entries); this->total_threads++; } } #endif for (int i = this->total_threads; i < count; i++) { entry = worker_create(this, (thread_main_t )process_jobs); if (entry) { TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&this->threads, entry, entries); this->total_threads++; } } } else if (count < this->total_threads) { this->desired_threads = count; } pthread_cond_broadcast(&this->job_add); pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->mutex); } static void __processor_queue_job(processor_t *this, struct job_entry *entry){ pthread_mutex_lock(&this->mutex); TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&this->jobs, entry, entries); pthread_cond_signal(&this->job_add); pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->mutex); } static void __processor_execute_job(processor_t *this, struct job_entry *entry){ bool queued = false ; pthread_mutex_lock(&this->mutex); if (this->desired_threads && (this->total_threads > this->working_threads)) { entry->job->status = JOB_STATUS_QUEUED; TAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(&this->jobs, entry, entries); queued = true ; } pthread_cond_signal(&this->job_add); pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->mutex); if (!queued) { entry->job->execute(entry->job); entry->job->destory(entry->job); free (entry); } } processor_t *processor_create () { processor_t *this = NULL ; this = calloc (1 , sizeof (*this)); this->set_threads = __processor_set_threads; this->queue_job = __processor_queue_job; this->execute_job = __processor_execute_job; this->cancel = __processor_cancel; this->destory = __processor_destory; pthread_mutex_init(&this->mutex, NULL ); pthread_cond_init(&this->job_add, NULL ); pthread_cond_init(&this->thread_terminated, NULL ); TAILQ_INIT(&this->threads); TAILQ_INIT(&this->jobs); return this; } static job_requeue_t __job_exec(job_t *this){ job_requeue_t requeue; srand(time(NULL ) + pthread_self()); int timeout = rand()%10 ; sleep(timeout < 1 ? 1 : timeout); printf ("%ld [%s]\n" , pthread_self(), __func__); requeue.type = JOB_REQUEUE_TYPE_FAIR; return requeue; } static void __job_destory(job_t *this){ printf ("[%s]\n" , __func__); free (this); } static bool __job_cancel(job_t *this){ printf ("[%s]\n" , __func__); return true ; } int main (void ) { processor_t *processor = processor_create(); processor->set_threads(processor, 4 ); struct job_entry *entry1 =calloc (1 , sizeof (*entry1)); job_t *job1 = calloc (1 , sizeof (*job1)); job1->execute = __job_exec; job1->destory = __job_destory; job1->cancel = __job_cancel; entry1->job = job1; struct job_entry *entry2 =calloc (1 , sizeof (*entry2)); job_t *job2 = calloc (1 , sizeof (*job2)); job2->execute = __job_exec; job2->destory = __job_destory; job2->cancel = __job_cancel; entry2->job = job2; struct job_entry *entry3 =calloc (1 , sizeof (*entry3)); job_t *job3 = calloc (1 , sizeof (*job3)); job3->execute = __job_exec; job3->destory = __job_destory; job3->cancel = __job_cancel; entry3->job = job3; struct job_entry *entry4 =calloc (1 , sizeof (*entry4)); job_t *job4 = calloc (1 , sizeof (*job4)); job4->execute = __job_exec; job4->destory = __job_destory; job4->cancel = __job_cancel; entry4->job = job4; processor->queue_job(processor, entry1); processor->queue_job(processor, entry2); processor->queue_job(processor, entry3); processor->execute_job(processor, entry4); while (!getchar()); processor->destory(processor); return 0 ; }